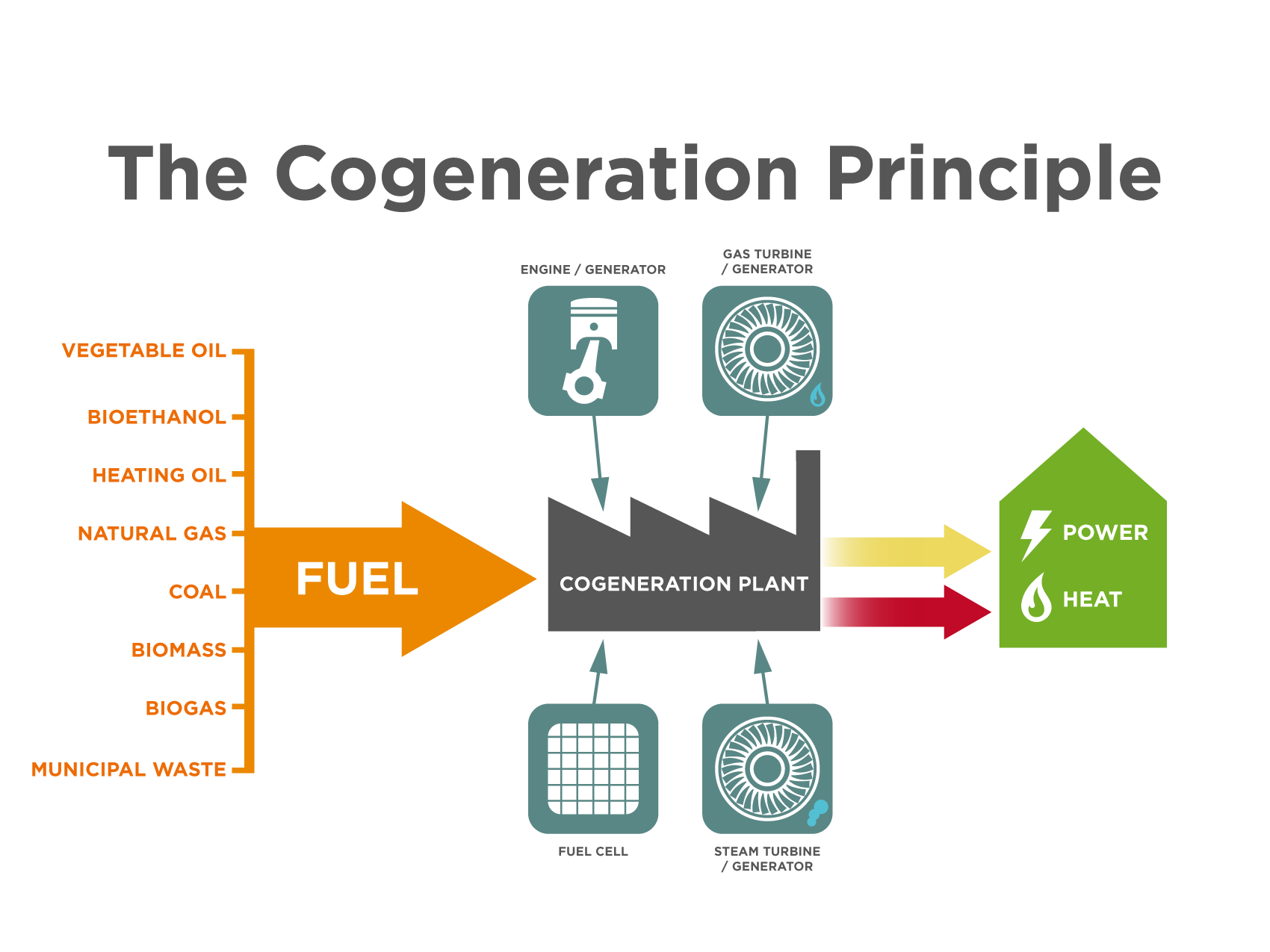
Cogeneration systems can work with both fossil fuels and renewable fuels
Cogeneration units can work with a variety of fuels, all of which offer unique environmental benefits compared to traditional technology alternatives.
According to the ECB 2012 data, in Europe, natural gas is the most used fuel in cogeneration with a share of 49.5%.
Natural gas fueled applications:
Natural gas offers many benefits, such as high heating value, convenient fuel cost and availability at many locations. In addition, it is a clean fuel with low carbon content. It produces 40 to 50% less CO2 than coal-fired CHP. These properties make natural gas an outstanding fuel in many cogeneration systems.
Some cogeneration plants run on petroleum products and derivatives, petcoke, lignite and coke type coals.
Heating oil;
Heating oil has a high energy content per volume and is very easy to transport and store.
Source: www.theade.co.uk
Renewable energy-fed cogeneration combines the advantages of environmental sustainability with maximum energy efficiency.
Biomass for energy and heat production;
The combustion of solid biomass (obtained from the ostrich) for heat production is the main CHP bioenergy route in the world, following a continuous pathway to reduce productivity and pollutant emissions. Depending on the size, several systems can be considered. Small-scale heating systems for households typically use wood or pellets. While medium-sized users often burn wood chips in grate boilers, large-scale boilers can burn wider fuel types, including those thrown from waste woods and thrown out. Heat can be produced at medium or large scale through cogeneration; it provides steam for industrial processes and can supply heat networks.
Biogas fueled applications:
Many small and medium-sized cogeneration systems operate with biogas.
Biogas can be obtained from city-waste/landfill, animal and chicken manure and sewage residues.
Biogas is very environmentally friendly gas….it does not produce carbon emissions.
Biodiesel fueled applications:
Today, biodiesel fuel is produced by biomass with vegetable oils (such as rapeseed oil). The future spread of biodiesel will increase in cogeneration usage and will be competitive in terms of price.
Geothermal:
One of the widespread systems is to use the heat from geothermal sources connected to a cogeneration unit.
The geothermal fluid taken from underground feeds a power plant that, if the temperature and flow of geothermal fluid permits, produces energy electricity and gives the residual heat to the district heating network.
The cogeneration geothermal systems are very flexible and can produce electricity in summer, when heat is not needed, and deploy heat in winter.